Citation
Falzone, G.; Puerta Falla, G.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, M.; Kumar, A.; Bauchy, M.; Neithalath, N.; Pilon, L.; Sant, G. Cement and Concrete Composites 2016, 71: 153-65.
Falzone, G.; Puerta Falla, G.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, M.; Kumar, A.; Bauchy, M.; Neithalath, N.; Pilon, L.; Sant, G. Cement and Concrete Composites 2016, 71: 153-65.
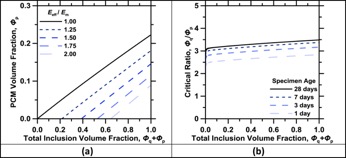
The embedment of microencapsulated phase change materials (PCMs) is a promising means for improving the thermal inertia of concrete. However the addition of such soft microcapsules degrades the mechanical properties, i.e., the elastic moduli and compressive strength, of cement-based composites. This study experimentally quantifies the effects of stiff quartz inclusions and soft PCM microcapsules, individually, and when added together, on the mechanical properties of cementitious composites. In addition, a variety of effective medium approximations (EMAs) were evaluated for their ability to predict the experimentally measured composite effective moduli. The EMAs proposed by Hobbs and Garboczi and Berryman (G-B) reliably estimate experimental data. The experimental data and the EMAs were applied to develop a design rule for performance equivalence, such that the composite modulus of elasticity can be maintained equivalent to that of the cementitious paste matrix, in spite of the addition of soft PCM microcapsules.