Citation
Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Yu, Y.; Valenzano, L.; Bauchy, M.; Sant, G. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2015, 119(46), 25991-25999.
Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Yu, Y.; Valenzano, L.; Bauchy, M.; Sant, G. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2015, 119(46), 25991-25999.
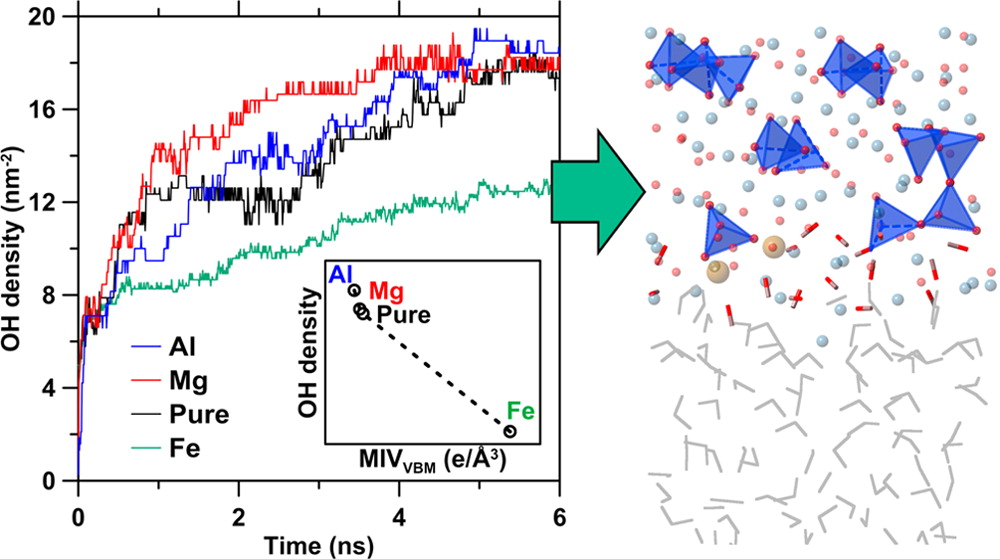
Systematic manipulation of the reactivity of silicate materials in aqueous environment remains a challenging topic. Herein, by combining first-principles and reactive molecular dynamics simulations, we present a complete picture of the influence of impurity species on hydration reactivity, using the reactive triclinic tricalcium silicate phase as an example. We show that although initial hydration is influenced by the surface’s chemistry and structure, longer-term hydration is primarily controlled by proton transport through the bulk solid. Both shorter- and longer-term hydration processes are noted as being intrinsically correlated with electronic features. These outcomes provide the first direct evidence of the linkages between electronic structure and the longer-term (i.e., on the order of several nanoseconds) hydration behavior and sensitivity of hydrophilic crystalline materials and also offer a pathway to efficient compositional design for similar materials.