Citation
Wei, Z.; Falzone, G.; Wang, B.; Thiele, A.; Puerta-Falla, G.; Pilon, L.; Neithalath, N.; Sant, G. Cement and Concrete Composites 2017, 81: 66-76.
Wei, Z.; Falzone, G.; Wang, B.; Thiele, A.; Puerta-Falla, G.; Pilon, L.; Neithalath, N.; Sant, G. Cement and Concrete Composites 2017, 81: 66-76.
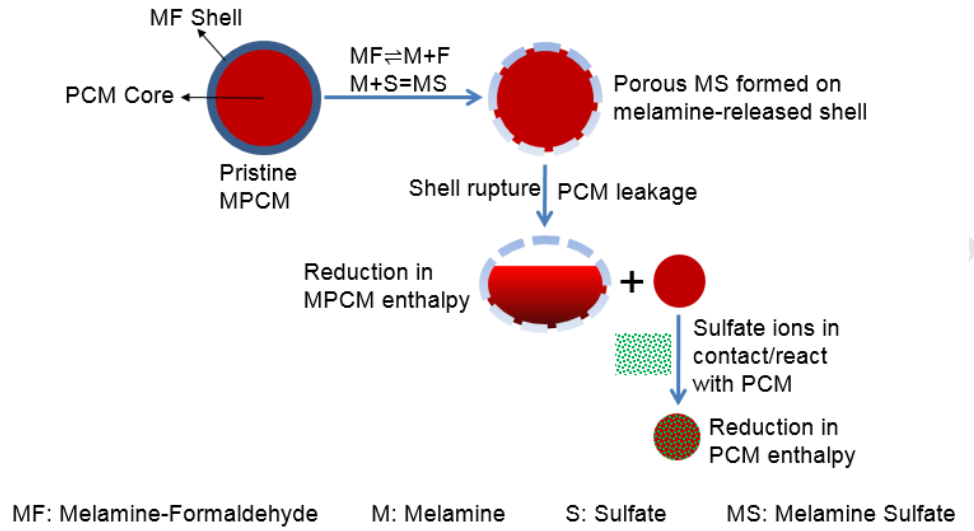
This study investigates the durability of cementitious composites containing microencapsulated phase change materials (PCMs). First, the stability of the PCM’s enthalpy of phase change was examined. A reduction of around 25% in the phase change enthalpy was observed, irrespective of PCM dosage and aging. Significantly, this reduction in enthalpy was not caused by mechanical damage that was induced during mixing, but rather by chemical interactions with dissolved SO42- ions. Second, the influence of PCM additions on water absorption and drying shrinkage of PCM-mortar composites were examined. PCM microcapsules reduced the rate and extent of water sorption; the former was due to their non-sorptive nature which induces hindrances in moisture movement, and the latter was due to dilution, i.e., a reduction in the volume of sorptive cement paste. On the other hand, PCM inclusions did not influence the drying shrinkage of cementitious composites, due to their inability to restrain the shrinkage of the cement paste. The results suggest that PCMs exert no detrimental influences on, and, in specific cases, may even slightly improve the durability of cementitious composites.